If you have a remote branch, you likely have a local branch with the same name. A typical workflow is to first make commits locally and then push those changes to the remote branch.
However, sometimes you need to push to a different remote branch. In order to do this in Git, you will need to change the upstream of your local branch to your new target remote branch.
“I use @GitKraken because I can concentrate on getting the job done rather than trying to remember the commands and trying to imagine how the branches connect.” – @palmiak_fp
How do you set an upstream branch in GitKraken?
With GitKraken, it’s easy to locate a branch and change the upstream in Git to push, pull, or fetch from a different Git branch.
Right-click on a branch to set the upstream or click the ellipsis icon.
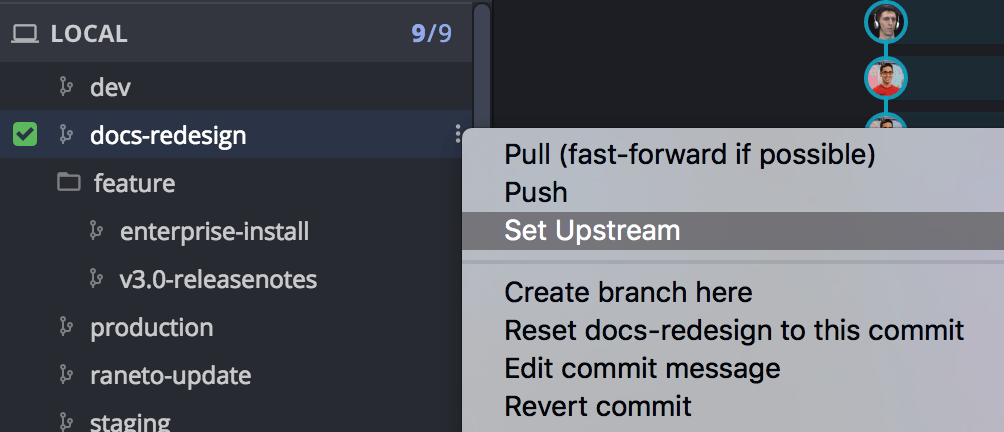
Alternatively, you can drag-and-drop a branch from the central graph in GitKraken to push instead of setting upstream.
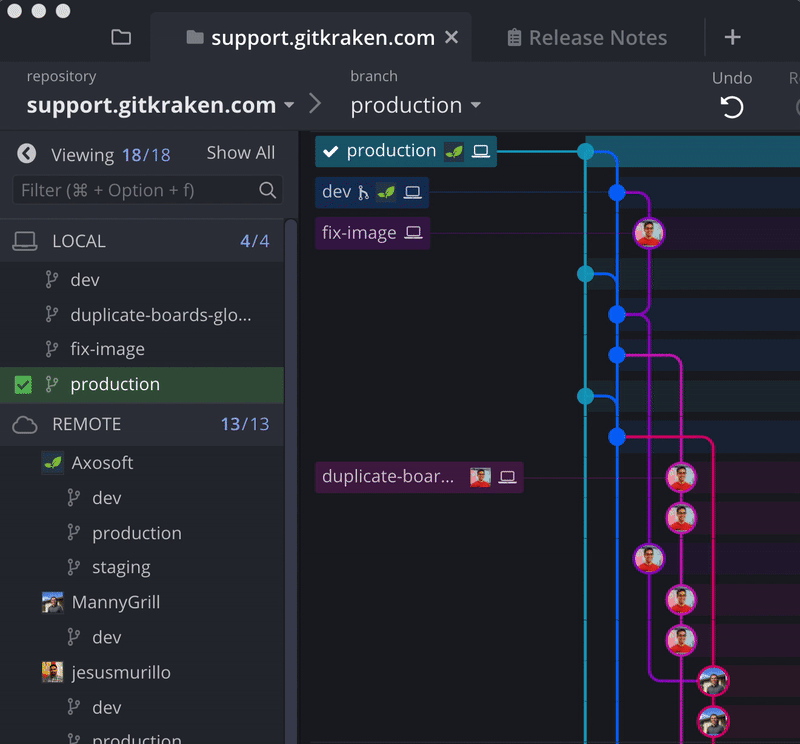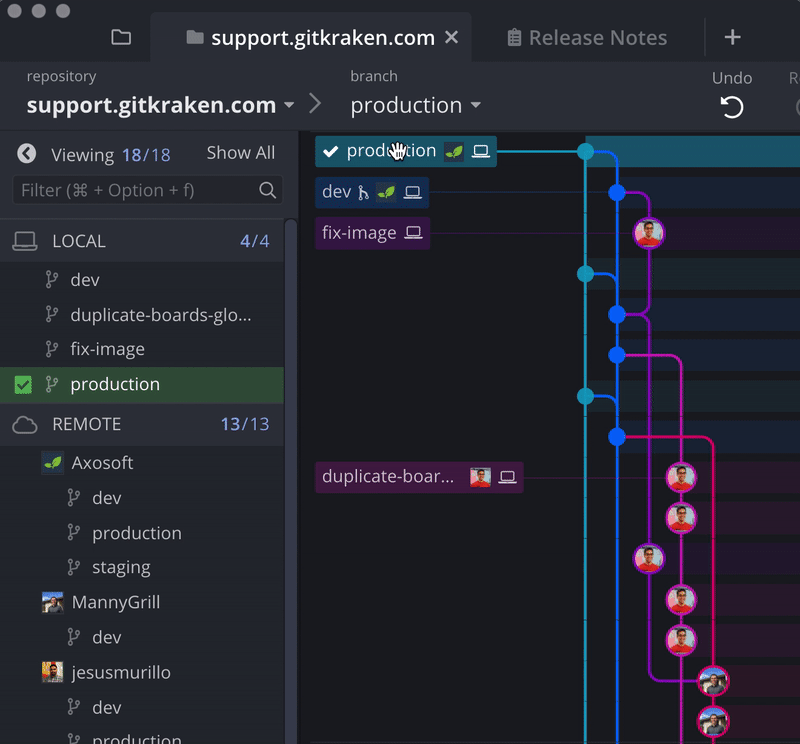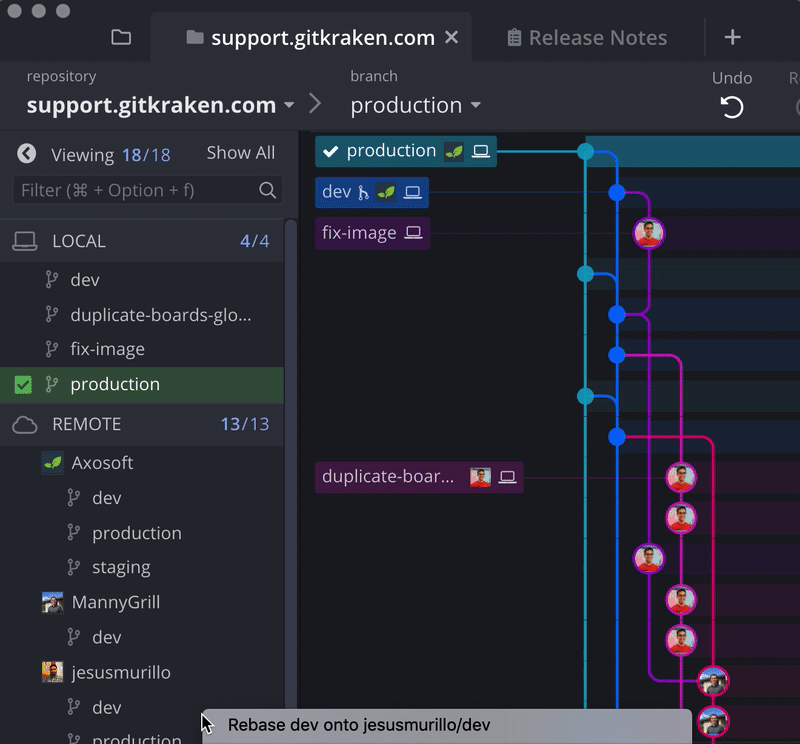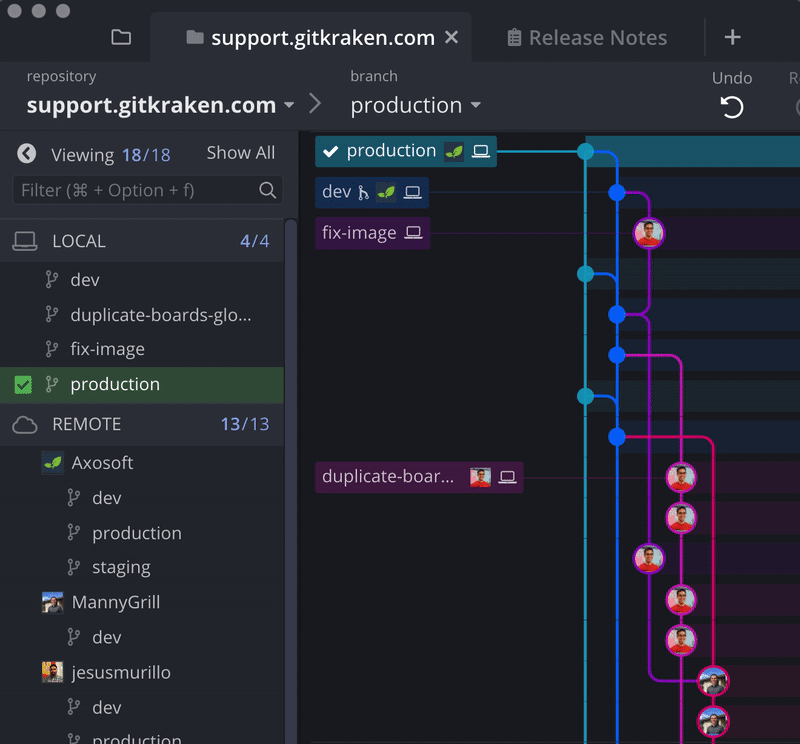
Daily Git actions, like push, pull, fetch, and setting upstream are easier with GitKraken, thanks to the incredible visual context offered by the central graph. You’ll always know what’s going on with your commits, branches, and remotes. 💥
How do you set an upstream branch in Git using the command line?
To set the upstream branch in Git, use the following command:
$ git push --set-upstream <remote> <branch>This will push your local branch to the new remote branch.
 GitKraken MCP
GitKraken MCP GitKraken Insights
GitKraken Insights Dev Team Automations
Dev Team Automations AI & Security Controls
AI & Security Controls